
In today’s world full of uncertainties, not all trends are worth focusing on—we need to seize the most important and widely influential ones. Euromonitor International has released the white paper “Five Cross-Industry Transformation Trends for 2026: Reshaping Strategy and Growth.” This article will break down these five core trends in detail, helping enterprises understand and grasp future market directions to maintain competitiveness in the coming year.
The five trends are:
- Next-Gen Online Retail: Optimizing shopping experiences and market entry strategies
- Beyond Low Prices: Breaking price positioning to deliver and realize value-added services
- Market Volatility: Uncovering growth opportunities and managing risks in a turbulent economy
- Path to Longevity: Understanding health needs across different life stages to accurately match diverse demands
- Purpose-Driven Consumption: Integrating product innovation with emerging consumption scenarios and demand states
This is the second installment, providing an in-depth interpretation of “Market Volatility.”
The global market is becoming increasingly unstable: trade disputes, geopolitical tensions, and climate change… If Trump’s tariff policies develop in a pessimistic direction, the global real GDP growth rate between 2026 and 2027 may drop by 2.8 percentage points compared to the baseline forecast. For enterprises, it is crucial to manage risks and enhance resilience now. At the same time, flexible pricing strategies and innovation are key to seizing new opportunities. Targeting fast-growing emerging markets such as India and Vietnam can help boost sales and diversify supply chains.
1. Tariffs, Geopolitical Tensions, and Climate Change Are the Main Drivers of Market Volatility
Since Trump was re-elected U.S. President in January 2025, global economic uncertainty has increased significantly due to various changes in his trade and other policies. Although there has been some progress in trade negotiations, U.S. trade policy remains unclear. Coupled with the possible escalation of global trade wars, many risks are still a concern. Meanwhile, ongoing geopolitical tensions—such as the Russia-Ukraine war and the Iran-Israel conflict—continue to pose challenges to commodity prices and global supply chains. Climate change has exacerbated these issues: extreme weather around the world has affected commodity supplies to a certain extent. Therefore, the economic outlook is very uncertain, with unstable prices and numerous trade challenges.

2. The Future Requires Sharp Forecasting and Proactive Risk Management
The global growth outlook remains unclear in the short and medium term, and differences between major markets are widening—especially between developed and developing economies. Global economic growth is expected to slow from 3.3% in 2024 to 2.9% in 2025, with a still grim prospect facing multiple risks, including fluctuations in Trump’s policies. Due to slowing economic growth and rising recession risks, consumer confidence in the U.S. and Europe may decline further, leading to more cautious spending behavior and a greater focus on cost-effectiveness.
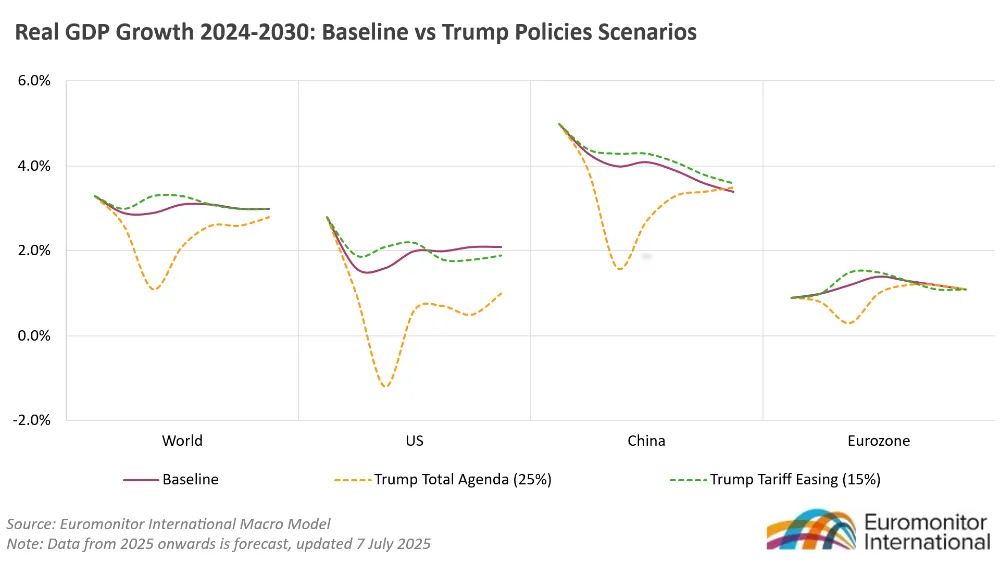
Volatility in both the macroeconomy and consumer demand is intensifying, making corporate planning more complex. This highlights the need to improve market forecasting capabilities, conduct multi-scenario planning, and proactively avoid risks. However, opportunities still exist in countries that maintain steady growth and expanding domestic markets, such as India and Vietnam. Global FMCG giants like Unilever and Nestlé have proven that leveraging India’s economic resilience is a successful strategy.
3. Trade and Tariff Wars Highlight the Need for Risk-Resilient Supply Chains
Changes in the global trade pattern and future uncertainties in U.S. trade policy may drag down global supply chains. In the worst-case scenario, new U.S. tariffs could cost U.S. businesses up to $1.2 trillion and increase the cost of parts purchased between enterprises by as much as 20%. This situation will put additional pressure on corporate finances and accelerate the restructuring of global production networks.
Therefore, enterprises now value supply chain security more than just cost. This will continue to drive production diversification, efforts to “reshore” manufacturing, and investment in automation and digital tools to improve operational efficiency. For example, after the tariff policy announcement in March 2025, Hyundai Motor Company committed to investing $21 billion in local production in the U.S.—both to avoid future tariffs and to strengthen its supply chain layout in the country.
4. Flexible Pricing and Alternative Sourcing Are Key to Coping with Cost Volatility
Price pressures remain uneven across markets, and risks are rising, making it increasingly difficult for enterprises to manage pricing strategies effectively. Although falling energy prices and weakened demand since the start of 2025 have helped ease inflationary pressures, higher tariffs and ongoing supply chain disruptions are pushing up costs—especially in the U.S. In addition, climate-related shocks have led to soaring commodity prices, such as cocoa and oranges, since 2024.
The global beverage price index is expected to reach 216 by 2025 (2010 = 100), up from 176 in 2024.
Source: Euromonitor International
Amid slowing growth and persistent cost pressures, operational efficiency remains a top priority for enterprises in the short and medium term. To cope with price volatility, companies like Shein and Walmart are adopting technology-supported flexible pricing strategies to protect profits and respond quickly to market changes. At the same time, alternative materials and products that offer more cost-effective and stable supply sources are gaining opportunities.
Economic uncertainty has become the new normal, and we should view it as a catalyst to become more resilient and innovative. To cope with future volatility and turn challenges into opportunities, building a flexible response system—driven by data analysis, scenario planning, and in-depth market and consumer insights—will become increasingly important for global enterprises.
